4141: 插入排序(sort)
题目描述
插入排序是一种非常常见且简单的排序算法。小 Z 是一名大一的新生,今天 H 老师刚刚在上课的时候讲了插入排序算法。
假设比较两个元素的时间为 ,则插入排序可以以 () 的时间复杂度完成长度为 的数组的排序。不妨假设这 个数字分别存储在 , , · · · , 之中,则如下伪代码给出了插入排序算法的一种最简单的实现方式:
这下面是 C/C++ 的示范代码
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = i; j>=2; j‐‐)
if ( a[j] < a[j‐1] ){
int t = a[j‐1];
a[j‐1] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
} 为了帮助小 Z 更好的理解插入排序,小 Z 的老师 H 老师留下了这么一道家庭作业:
H 老师给了一个长度为 的数组 ,数组下标从 开始,并且数组中的所有元素均为非负整数。小 Z 需要支持在数组 上的 次操作,操作共两种,参数分别如下:
: 这是第一种操作,会将 的第 个元素,也就是 的值,修改为 。保证 ≤ ≤ , ≤ ≤ 。 注意这种操作会改变数组的元素,修改得到的数组会被保留,也会影响后续的操作。
: 这是第二种操作,假设 H 老师按照上面的伪代码对 数组进行排序,你需要告诉 H 老师原来 的第 个元素,也就是 ,在排序后的新数组所处的位置。保证 ≤ ≤ 。注意这种操作不会改变数组的元素,排序后的数组不会被保留,也不会影响后续的操作。
H 老师不喜欢过多的修改,所以他保证类型 的操作次数不超过 。
小 Z 没有学过计算机竞赛,因此小 Z 并不会做这道题。他找到了你来帮助他解决这个问题。
输入
输入的第一行包含两个正整数 , ,表示数组长度和操作次数。保证 ≤ ≤ , ≤ ≤ * 。
输入的第二行包含 个空格分隔的非负整数,其中第 个非负整数表示 。保证 ≤ ≤ 。 接下来 行,每行 ∼ 个正整数,表示一次操作,操作格式见题目描述。
【数据范围】
对于所有测试数据,满足 ≤ ≤ , ≤ ≤ ×, ≤ ≤ , ≤ , ≤ 。
对于所有测试数据,保证在所有 次操作中,至多有 次操作属于类型一。
各测试点的附加限制及分值如下表所示。
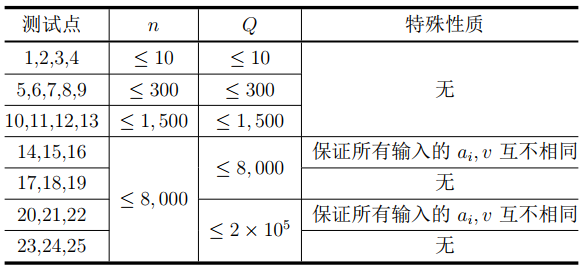
输出
样例输入 复制
3 4
3 2 1
2 3
1 3 2
2 2
2 3样例输出 复制
1
1
2提示
【样例 1 解释】
在修改操作之前,假设 H 老师进行了一次插入排序,则原序列的三个元素在排序结束后所处的位置分别是 , , 。
在修改操作之前,假设 H 老师进行了一次插入排序,则原序列的三个元素在排序结束后所处的位置分别是 , , 。
注意虽然此时 = ,但是我们 不能将其视为相同的元素。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int id,num;
}a[8010];
int n,q;
bool cmp(node a,node b) {
if(a.num==b.num)
return a.id<b.id;
else
return a.num<b.num;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
scanf("%d",&a[i].num);
a[i].id=i;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp);
int op,u,v;
while(q--) {
scanf("%d",&op);
if(op==1) {
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
if(a[i].id==u) {
a[i].num=v;
break;
}
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp);
}else{
scanf("%d",&u);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
if(a[i].id==u){
printf("%d\n",i);
break;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=8e3+10;
struct node{
int id,val;
}a[N];
int n,q,Map[N];
void insert(int pos){
while(pos>1) { //从pos位置向前扫描,插入到适当位置
if(a[pos].val>a[pos-1].val) break;
if(a[pos].val==a[pos-1].val && a[pos].id>a[pos-1].id) break;
swap(a[pos],a[pos-1]);
Map[a[pos].id]=pos;
pos--;
}
while (pos<n) { //从pos位置向后扫描,插入到适当位置
if (a[pos].val<a[pos+1].val) break;
if(a[pos].val==a[pos+1].val && a[pos].id<a[pos+1].id) break;
swap(a[pos],a[pos+1]);
Map[a[pos].id]=pos;
pos++;
}
Map[a[pos].id]=pos;
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>q;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>a[i].val;
a[i].id=i;
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,[&](node A,node B){
if(A.val!=B.val) return A.val<B.val;
return A.id<B.id;
});
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) Map[a[i].id]=i;
int opt,u,v;
while(q--) {
scanf("%d",&opt);
if(opt==1){
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
a[Map].val=v;
insert(Map);
}else {
scanf("%d",&u);
printf("%d\n",Map);
}
}
return 0;
}